Introduction:
Acquired mutations in SF3B1 gene in myeloid neoplasms are classically associated with the presence of RS in Pearl Stain, ineffective erythropoiesis, and favorable prognosis. Nevertheless, in up to 20-25% of adults diagnosed with MDS with RS (WHO 2017), mutations in SF3B1 are not found, and molecular grounds for the presence of RS remain to be ascertained. The objective of our study was to investigate whether the presence of RS could be associated with germline variants in genes responsible for congenital sideroblastic anemia (CSA).
Methods:
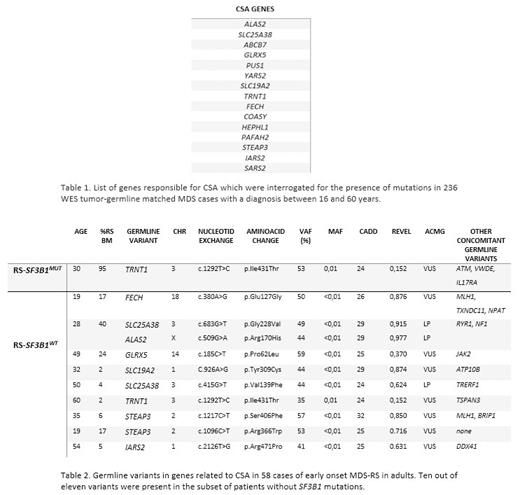
Patients diagnosed with de novo MDS between 16-60 years of age without previous organ dysfunction were recruited from 32 centers of GEMSD since 2016. Whole exomes were sequenced using HiSeq4000-NovaSeq6000-Illumina, paired tumor-germline samples. Mean depth was 100x, with 150 million reads per sample and quality Q30a>95%. Variants were analyzed using a bioinformatics pipeline: filtering intronic and synonymous variants and those with a population frequency >1%. The mutational state of SF3B1 was determined by Sanger Sequencing and Next Generation Sequencing (NGS). Germline variants were categorized according to American College of Molecular Genetics (ACMG) criteria. The list of genes related to CSA explored in this study is shown in Table 1.
Results:
Among 239 cases of adults diagnosed with early-onset MDS (mean age at diagnosis: 48 years, range 16-60), 58 (24%) patients presented with RS in bone marrow (mean RS: 28%). Of these 58 patients, acquired mutations in SF3B1 were not found in 32 (55%). Nine out of these 32 (25%) harbored a germline variant (two variants in one case) in genes responsible for CSA (Table 2): SLC25A38 (n=2), STEAP3 (n=2) FECH, ALAS2, GLRX5, SLC19A2, TRNT1 and IARS2. This frequency was statistically higher than in the SF3B1 and RS mutated group (n=23), with only one case with a germline variant in a CSA gene (p=0.013). It was also higher than in the non-RS cases (n=181), with only one case in this group (p<0.001). Using the Fisher's exact test, commonly used to perform enrichment, the odds ratios were also significant (p=0.033 and p<0.0001), respectively.
Among patients with RS, those carrying a CSA gene germline variant were younger (43 vs. 54 years, p=0.04), had a higher rate of neutropenia (1.8 vs. 2.6 x 10E9/L, p=0.02), and thrombocytopenia (151 vs. 259 x 10E9/L, p=0.03) than MDS-RS patients with SF3B1 mutated. Furthermore, MDS-RS with a germline variant in CSA genes had a lower mean percentage of RS than patients who acquired the mutation in SF3B1 (14% vs. 38%; p=0.003).
Conclusions:
In our series, the frequency of MDS-RS without SF3B1 mutations is higher in early-onset adult MDS than the one reported in MDS in advanced age. Whole exome analysis allowed us to describe, for the first time, a significant enrichment of variants in genes causing CSA in young adults with RS and without acquired mutation in SF3B1.
Disclosures
Tormo:Pfizer: Honoraria; AbbVie: Honoraria; Astellas: Honoraria; BMS: Honoraria; MSD: Honoraria. Bosch:BeiGene: Consultancy; Roche: Honoraria; Lilly: Consultancy; Mundipharma: Consultancy, Honoraria; Gilead: Consultancy, Honoraria; Janssen: Consultancy, Honoraria; AbbVie: Consultancy, Honoraria; Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria; AstraZeneca: Consultancy, Honoraria; Takeda: Consultancy, Honoraria; Karyospharm: Other; Celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria; Roche: Consultancy, Honoraria. Diez-Campelo:BMS/Celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Advisory board fees; Gilead Sciences: Other: Travel expense reimbursement; Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; GSK: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Jerez:Novartis: Consultancy; Astrazeneca: Research Funding; GILEAD: Research Funding; BMS: Consultancy.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal